The possible uses of terahertz technology, which is still in its infancy but is rapidly expanding, range from airport passenger scanning to massive digital data transfers. Significant scientific developments have been reflected by it. Three distinct characteristics of terahertz (THz) radiation encourage the growth of the whole terahertz sector.
The remaining portion of the electromagnetic wave spectrum that hasn’t been scientifically and economically exploited is the terahertz (THz) frequency range (0.1 THz – 3 THz). Because of this, the term “terahertz gap” is frequently used in literature to describe the terahertz frequency range. The potential uses for this frequency range are exciting for various applications, which are also widely recognized.
Terahertz technology is increasingly being used in the healthcare industry, including for spectroscopy-based cancer diagnosis, terahertz imaging, and biomedical imaging, among other uses. Furthermore, several chronic illnesses and associated conditions have been easily detected thanks to the capability of terahertz radiation to provide high-quality spectroscopic imaging.
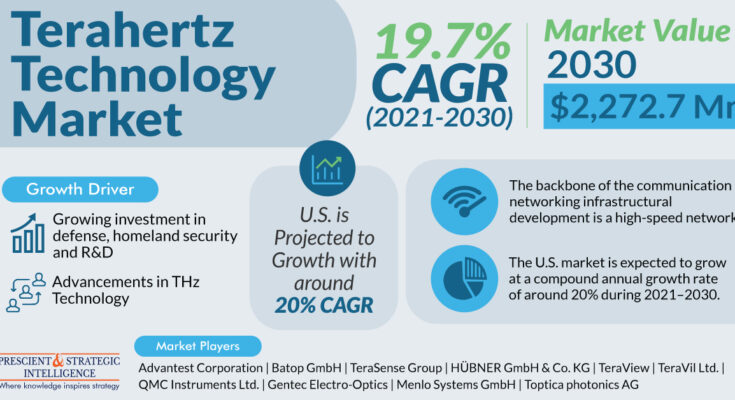
Thus, it is expected that by 2030, the value of sales for terahertz technology will be $2,272.7 million. The expansion of THz technology’s uses in communications systems, medicinal treatments, and security and safety solutions can support the growth.
Terahertz radiation has made significant strides toward becoming a standard in the healthcare sector by replacing traditional x-rays and infrared rays. There is an urgent demand for effective solutions due to the rising security system issues in various sectors. THz technology has mostly been used in applications like non-destructive testing and security imaging.
Furthermore, because most objects have distinctive spectral characteristics in the terahertz region and can be categorized by authorities, terahertz technology may detect toxic substances from a great distance.
Terahertz is unique in that it may be utilized for security in high-risk areas by providing a full description of the item through the combination of spectral imaging and identification.
The capacity to find and recognize items concealed behind obstructions is one of THz technology’s key capabilities. Terahertz lasers may now be used to find harmful non-metallic items like ceramic blades or plastic bombs at airports and other locations that require high levels of security. T-rays may pass through clothing but not the top skin, making this conceivable.
X-ray bag scanning and metal detection are laborious procedures that are more challenging in areas with high traffic from public transit.
Therefore, technical advancements that enable security checks to be made even when the suspected source is far away are required. A huge number of persons can be scanned using terahertz equipment without having to stop for a safety check. So, providing a response to these difficulties.
Being able to recognize dangers like body-worn explosives and hidden weapons has become increasingly important in recent years as security needs have grown. Terahertz technology has lately seen a rise in attention for defense-related and security applications due to the rising emphasis on imaging hidden bombs.
Potential uses for THz sensors in the military for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) include locating lone individuals behind adversarial lines, establishing targets, and terminal guiding of precise weapons.